Conventional antivirus application is practically ineffective when it comes to contemporary viruses. Signal based detection – in signature based detection your security software compares the files to a known malware database – your security misses between 80-90 percent of actual attacks. Why? Since intruders only have to make minor adjustments to their code, and poof, the signature does not match.
It is there that behavior analysis turns it all around. Rather than querying a system on whether or not this file is a known threat, the AI-based systems query on whether or not this process is acting suspicious. The difference is massive. It will be detected by behavioral detection when a registry-legitimate Windows utility begins to encrypt files at 3 AM without any warning. Traditional antivirus? Has no problem with this since the tool is not bad.
In this article, an analysis of how AI prevents advanced attacks is given, which involves behavior monitoring rather thanSignature chasing. This is what’s happening nowadays in the area of threat detection, whether you are in security operations, development, or perhaps you are just interested in knowing how modern defense works.
Table of Contents
Foundations of Behavioral Analysis: Establishing Normal Baselines
The fundamental idea of behavioral analysis is a basic one: one cannot recognize abnormal behaviour unless he/she has the concept of normal at his/her disposal.
The machine learning systems take a minimum of 90 days to be idle. Through this base, the artificial intelligence monitors all the user activities, all the process executions, all the network connections. It is constructing a behavioral profile of each object in your environment humans, service accounts, applications, devices.
The following things can be tracked at the time of set baselines:
User behavior patterns:
- Login times and locations
- Applications used and time of use.
- Frequencies and volumes of file access.
- Connection of networks that occurred.
- Command-line tool usage
System behavior patterns:
- Parent child relationships Process Processes.
- Registry modifications
- Directions of traffic and amount of traffic on the network.
- Memory allocation patterns
- File system operations
The AI does not just document averages. It creates statistical models which explain the variance Monday mornings are not the same as Friday afternoons, tax season is not the same as summer, developers are not the same as accountants.
These peer group comparisons are important since no one would consider flagging down a database administrator who is asking queries to databases as making sense, but on the other hand, flagging down a marketing coordinator who has done the same thing is of absolute sense.
Patience is an obstacle during the creation of the baseline. Companies cannot produce high-confidence alerts when the system is in its process of learning. In companies that follow seasonal cycles, such as retail during the holidays, tax companies during filing season, then, building up the meaningful baselines may take six months. Hurry this step and the awareness of false positives rises.
Adaptive baselines are being used in the modern systems which constantly evolve. Behavioral models automatically retrain when your infrastructure alters when workers switch roles when new applications are installed. Developing environments are very dynamic and the static baselines are overtaken within weeks.
Machine Learning Classification of User and Process Behavior
At this point, the classification algorithms take over after the baselines are present. Such are not mere rule engines; they are complex ML models that process hundreds of behavioral measurements at the same time.
Isolation Forest algorithms subdivides behavioral data into decision trees which isolate anomalies quickly and isolated unusual data does not need training data with labels. Isolation Forest highlights the incident in milliseconds when the network traffic of a particular user is redirected against what the user is known to have done in a regular pattern.
Neural networks that reduce and rebuild behavioral data are called autoencoders and are also good at identifying minor anomalies in the high-dimensional landscape of a cloud infrastructure. Such systems are conditioned to the shape of normal behavior. In cases where the reconstruction accuracy decreases due to the fact that the current behavior is not corresponding to the learned pattern, alerts are triggered.
Clusters such as K-means and DBSCAN automatically isolate and differentiate deviant and normal behaviors. Any user, the behavior of which lies outside of all predefined clusters, initiates inquiry.
Examples in real life: Microsoft Defender ATP is a combination of pre-execution blocking and post-execution behavior observing. Sandboxing is first done to unknown executables.
When in operation, it can disseminate suspicious sequence behavior trees of parent processes giving birth to children, allocating memory, calling APIs and submitting them to cloud-based ML classifiers to obtain real-time verdicts. This method will detect zero-day malware which signature-based detection would fail to identify all together.
Conventional security solutions consider single action separately. ML of behavior is action-relationship evaluation. One command of PowerShell can be harmless; PowerShell downloading a file, in turn, creating a scheduled task, and changing the registry keys? It is an attitude that displays compromising.
Detecting Insider Threats Through Behavior Pattern Deviations
One of the most expensive security issues is insider threats, which cost on average, 23.8 million dollars per organization per year based on current research. This is the exact issue that behavioral analytics addresses since insiders work under valid credentials.
This is what insiders can be noticed by the behavior:
Violations of access patterns: When an employee who accesses 10-15 records daily in the past, accesses suddenly 5, 000 records. The credentials are valid, it is technically authorized access but the volume deviation identifies exfiltration attempt scream.
Temporal anomalies: Access by users who do not always work regular business hours (during the night and Mondays). Geographic anomalies are an instance where one is logging in to locations that do not resonate with their travel history or geographic location.
Clustering indicators: Users that are accessing those systems that they do not usually access. The involvement of a member of the finance team in the development servers creates instant alarms.
Data processing modifications: Email messages where a user never prints the documents and printer suddenly starts transferring files, or files that employees usually cannot access via USB transfer on gigabytes in very short time.
The behavioral approach captures the gaps in the traditional access controls. It may be that a user has permission to do something but the patterns used determine the intentions. In the case of an employee leaving the company and beginning to systematically copy intellectual property several weeks before they resign, behavioral analytics identifies the preparation stage before it will cause harm.
The complexity here is in the ability to sort out the maliciousness of the behavior and the justifiable role changes. The access patterns of an employee who is promoted to a new position will be different of course. Quality behavioral systems will include HR data promotions, transfers, role changes so that baselines are changed dynamically and false positives during legitimate transitions are prevented.
Living-Off-the-Land Attack Detection (Abusing Legitimate Tools)
Living-off-the-land (LOtL) attacks relies on the use of the legitimate system facility powershell, wmi, psexec, certutil to escape notice. The signature-based security does not find anything questionable since the tools used are trusted.
Behavioral detection is best in this situation since it does not detect the use of tools, but the usage of the tools. admin and -ig commands: box and workspace exhibited suspicious flagged actions (with offensive pattern observed in the last three instances).
Suspicious PowerShell Signatures:
- admin and -ig commands: box and workspace had pattern behavior that was flagged suspicious (obvious pattern observed in prior 3).
- Base64 obfuscation (encoded commands).
- dude, script snatching downloads to cradles.
- By-passing the regular policies.
- Characteristics exasperated parent processes (Word or excel spawning PowerShell)
WMI abuse indicators:
- Creation of remote processes using WMI.
- Persistence services of event subscriptions.
- Abnormal query patterns to security-sensitive information.
Certutil weaponization:
- Downloading files with certutil (one of the lawful applications is the management of certificates).
- Encoding/decoding payloads
- Certutil based implementation chains with scripting interpreters.
There are real attacks that confound various legitimate tools together in sequences that each would be considered normal but then again, once it is put together, it is then considered compromised. These chains are analysed by behavioural systems.
The use of Excel macros that spawns PowerShell that is used to call certutil to download a file followed by the addition of a scheduled task to maintain itself may individually pass traditional inspections yet the behavior sequence is clearly malware.
This detection power also coexists with the AI Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems which monitor the behavior of endpoints at all times and cross-link event occurrences throughout the attack chain.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Identification Through Behavior Chains
APT groups are also unlike opportunistic attackers. They are tolerant, high-technology and deep-pocket. First compromise could not be carried out until months later as attackers charted networks, acquired privileges and persisted until they could code their plans.
Multi-stage attack pattern recognition: Behavioral analytics can detect the APTs:
There are two distinct reconnaissance stage behaviors, namely:
- Unusual external scanning of the networks.
- Domain enumeration queries
- Account credential testing Services.
- Interrogation of directory services.
Lateral movement patterns:
- Pass-the-hash attempts
- Kerberoasting activity
- Linking of SMB to various endpoints.
- Dumping Shows of credentials.
Persistence establishment:
- Registry run key adjustment.
- Scheduled task creation
- Service installation
- DLL hijacking preparations
The important observation here is that APTs drop behavioural trailmarks as long campaigns. The subject actions may be innocuous, such as an account of a service authenticated by the several servers may be just service administration but the cumulative pattern of reactions discloses the attack story.
APTs are especially vulnerable to graph-based anomaly detection. Such systems represent the user and system networks as graphs. The abnormal patterns of connections such as a rogue account attempting to communicate with areas of the network it had previously never interacted with become instantly apparent in graphs.
Companies that have behavioral analytics in place identify APTs 81.5% quicker than those using signature based recognition. Speed discrepancy is crucial since it either makes or breaks defenders to hold back the threat to the point of data exfiltration or before attackers accomplish the final goals.
Process Injection and Memory-Based Attack Detection
Fileless types of attacks are completely performed in memory that leaves very little as a forensic evidence. Attackers insert malware on-code into legal processes and conceal their presence within authorized applications.
The attacks can be detected by behavioral detection based on process behavior anomalies:
Injection indicators:
- Alterable processes assigning memory free of execute permissions.
- Memory access by cross process.
- Loads processes onto the DLLs that are not part of their standard library.
Whereas Injectible DLL patterns should exist to capture the ongoing trend of diverse plans, it is understanding that some alterations to the current build and operation framework of containers will be introduced (see Figure 2).Indicative DLL injection patterns.
Although there are to be existent patterns of assisted DLL injection patterns to consider the prevailing fashion of varying plans, it would be appreciable that certain changes imposed to the present or existing furnishing and functioning framework of containers will be asserted(see Figure 2).
Memory behavior anomalies:
- Abnormal memory page protection modifications.
- Heap spray patterns
- Chain Signatures Return-oriented programming (ROP) signatures.
- Shellcode execution_Features Shellcode execution Shellcode can be executed as code, binary code (binary machine code), or Mac code on the code interpreter.
Windows programs such as svchost.exe or explorer.exe must not communicate with foreign IP addresses across the network, they must not spawn unscheduled child programs and they must not execute coded scripts. The threat of behavioral monitoring of these deviations will show memory-based threats that cannot be detected by traditional file-based scanning at all.
State-of-the-art systems track behavior trees of processes that is, the children and parents of processes. A browser process which spawns PowerShell which spawns the creation of a cmd.exe process which spawns the creation of network connections is found to show compromise due to the ability to converse the chain of behavior despite the fact that any malicious files were not accessed by disk.
This is the primary feature of current AI-Powered Cybersecurity: Complete Guide applications, where threat detection in memory is now a minimum requirement in an effective defense.
Privilege Escalation Identification and Prevention
Virtually, attackers can hardly land with administrative privileges. The upgrade of privileges: being a regular user and turning into SYSTEM or root is a high risk and dangerous step towards attack, where behavioral systems take a particular interest.
Behavioral common escalators observed:
Token manipulation:
- Duplicating privileged tokens processes.
- SeDebugPrivilege abuse
- Unexpected context impersonation of tokens.
Exploit-based escalation:
- Loading of kernel drivers by use space programs.
- Abnormal system service interactions.
- Patterns used to define memory corruption tell us of attempted exploits.
Credential harvesting:
LSASS memory credential dump (credential dumping).
There is access to SAM database by-passing normal authentication.
Kerberos ticket manipulation The manipulation of Kerberos tickets.
Misconfiguration abuse:
- Binary service replacement endeavors.
- Path exploitation – unquoted.
- DLL search order hijacking
The behavioral detection identifies escalation attempts by comparing the privileges the processes are executing to those privileges they are requesting to obtain. Any regular user process trying to access LSASS memory or alter registry keys which require SYSTEM privileges generates an automatic alert.
Prevention component is stimulated when the behavioral risk scores become higher than the set levels. Adaptive systems do not need to wait until full compromise occurs, but they can automatically limit permissions, isolate endpoints/terminate suspicious processes before escalation occurs.
Data Exfiltration Patterns and Suspicious User Activities
The most crucial goal of most attackers is data theft. Exfiltration is detected in behavioral systems by
tracks of data movement abnormalities:
Volume-based indicators:
- However, enormous transfer of uploads to cloud storage.
- Massive transfer of files to third-party locations.
- Result sets that are large in comparison with historical norms as the result of database querying.
- Before transfer Compression of archives.
Timing anomalies:
- Access and transfer of data during off-hours.
- Quick-slap search e.g. over sensitive databases.
- Automated patterns of data collection.
Destination anomalies:
- Transfers to newly contacted foreign address space.
- Data transferred to individuals email inbox or cloud.
- There are unusual DNS queries, which indicate tunneling of data.
The modern exfiltration detection is sophisticated in knowing business context. It is natural that sales teams transfer customer information to CRM databases and theft is information sent to personal Dropbox. Behavioral models integrate application context, reputation of a destination as well as previous trends in order to differentiate between legitimate business operation and malicious exfiltration.
Behavioral analytics with data loss prevention (DLP) has allowed a significantly reduced false positive rate due to the complete removal of ambiguity commonly present in conventional DLP rules by behavioral context.
Adaptive Defense Mechanisms That Evolve With Threat Landscape
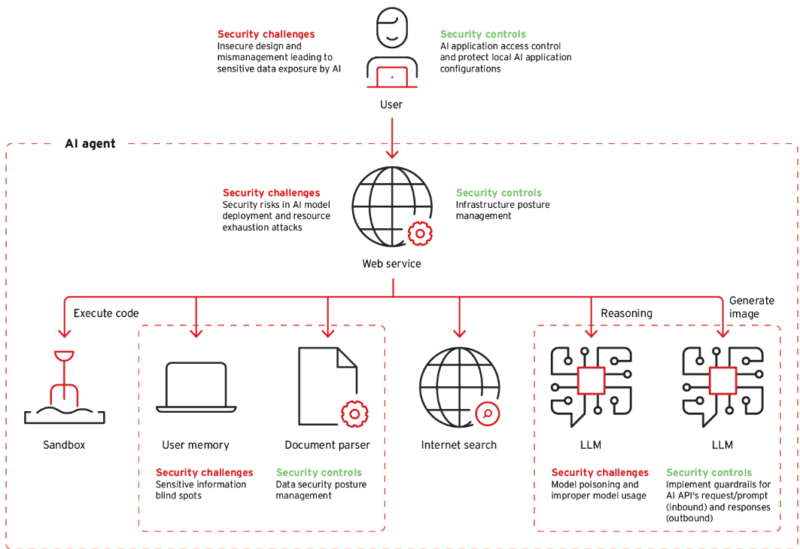
There is no chance that even the statical defenses can remain standing when attackers evolve. In the contemporary behavioral systems, there is the implementation of the continuous learning and adaptation:
Automated model retraining: ML models automatically retrain through new data as the organization behavior changes new applications learn new business processes, new workforce patterns, etc. This eliminates the model drift in which the accuracy in detection decreases with time.
Integration of threat intelligence: With new techniques of attacks appearing in the world, behavior systems has the capability of modifying the detection model, making the system adapt to new threats without the human need to modify the rule or pattern.
Federated learning methods: Federation (Federated learning) Organizations can enjoy the advantages of collective threats which involve behavioral models which learn by watching the attacks in more deployments without necessarily exchanging sensitive organizational information.
On-going automated red teaming: AI agents never stop attempting to penetrate the defenses but use the tactics of the attackers like an annual penetration test and identify the gaps before the actual threats can capitalize on them.
The current point of evolution is the Agentic AI Era. Independent security agents, which are not only detection algorithms but also reasoning systems that will investigate, prioritize, and act when they find threats, run at machine speed. Human investigators may need hours to investigate alerts yet autonomous investigators do not take longer than seconds.
This time delay will be existential in the case of AI-based attacks. The November 2025 campaign of the GTG-1002 exercise showed that swarm attacks with coordinated AI application achieved 80-90% of their attack life cycle independently. It takes machine-speed defense to counter machine-speed attacks.
Biometric Authentication Enhancements: Behavioral Patterns vs. Passwords
Passwords exemplify the knowledge-based authentication, which, by default, is prone to theft, phishing, and even credential stuffing. Behavioral biometrics involved a constant authentication process, which is predicated by intrinsic behavioral features.
Typing dynamics:
- Keystroke timing (dwell time) Keystroke timing(flight time)
- Typing rhythm and cadence
- Error correction patterns
- Common typo sequences
Mouse movement patterns:
- Acceleration and movement velocity.
- Characteristics of curves and angles.
- Click patterns and speeds
- Scroll behavior
Patterns of interaction of devices:
- Mobile device hold angles
- The intensity of touch and pattern of swipe.
- Switching behaviors about application switching.
- Preferences of navigation paths.
The most important advantage: such behavioral patterns are active not only at the moment of entry but throughout the system. When the credentials get stolen and an attacker makes successful authentications, all his actions are governed by behavior analysis, whose results show that the typing patterns, mouse movements and interaction patterns are different than expected in the legitimate profile of the user.
Behavioural biometrics have a false rejection rate of less than 2 percent when well tuned and prevent over 95 percent of account takeovers–by far outperforming password-based authentication.
Reducing Alert Fatigue Through Intelligent Behavior Modeling
The grimy truth of security operations around the globe: A majority of alerts are rubbish. Conventional rule based systems produce false positive results of more than 95%. In every one hundred alerts, 95-98 are benign activities that are false positives.
This has a trickle down market effect. On a day-to-day basis, analysts examine hundreds of false positives, which exhaust them easily. Threats that are real are ignored because analysts have been socialized to ignore such threats as the signal of a false alarm. Critical cases are not managed since there is no faith in the alert system.
Behavioral analytics solve this issue in several ways:
Peer group comparison: Under this approach, systems do not compare all users to universal baselines but make comparisons between users in comparable positions. This compensates legal role based differences, massively lowering false positives.
Contextual scoring: Behavioral systems do not issue an alert/no-alert, but first compute a risk score that uses business context, user history and present environmental factors.
Aggregation of alerts: Systems do not generate alerts one at a time: They determine which events are related to which case of investigation, thus minimizing the number of alerts but enhancing the context.
Explainable AI integration: SHAP (SHapley Additive explanations) values answer why some activities raised a warning signal, and allow an analyst to justify decisions in a short period of time and give a feedback, which facilitates better detection occurrences in the future.
Firms that use these methods get 60-80 percent false positives and 93 to 97 percent hits. The time savings on the part of the analysts 40% of the capacity should be diverted on the false positive investigation in this case, but rather on proactive threat hunting should yield ROI in terms of months.
Calibrating Detection Sensitivity for Your Environment
Nothing fits anything in behavioral detection. The levels of sensitivity to be applied in organizations depends on the risk sensitivity of their organization, business environment, and business reality.
Risk based tuning strategies:
High-security (financial services, healthcare, defense contractors): Smaller values of detection thresholds, do not mind a high false positive rate in favor of reducing false negative. False alarms are less expensive than false security.
High-volume operational setting (retail, hospitality): Detention lines are higher, of less importance to minimize false positives to ensure that the workload of analysts is still controllable. Concentration of critical threats.
Hybrid strategies: Various degrees of sensitivity to various asset classes. There are signal any of these thing Crown jewel systems: We perform aggressive interpretation. Value endpoints which are less valuable: We decrease the thresholds.
Time-varying adjustments: Bidirectionally time-varying adaptive detection sensitivity. Weird access logs may be innocent during working hours; the same requests at 3 AM are alarmed.
Calibration process is to take 6-12 months of continuous tuning. The organizations begin with settings of a defaulted vendor, calculate false positives and greatest accuracy of detecting the vendor, and progressively refine these settings and collect feedback of analysts. The feedback loop, where the system is trained by the analysts as a true/false positive and the alerts marked so, enhances the accuracy significantly.
Mature programs set measures of the number of alerts, the time spent by the analysts on each investigation, the average time to identify a real threat, and the levels of false positive cases by categories. These metrics are used to make calibration decisions and show ROI to the leadership.
Conclusion: Operational Imperative Behavioral Detection.
Consideration. Signature-based security is a corpse–yet to know it is dead. The attackers create polymorphic malware within a few seconds, launch new infrastructure within seconds, and use legitimate tools which the signatures will never pick.
The behavioral analysis is the inception of getting rid of the question is this file malicious and getting down to is this behavior suspicious. This difference makes the difference between organizations detecting threats within 15 days and 81 days, whether they intervene with privilege escalation before it occurs, whether they detect data theft during preparation before it occurs after exfiltration.
It has production-ready technology stack. There are open-source tools, such as Falco and Zeek that entry-level teams can use. AWS, Microsoft, and Google enterprise platforms incorporate behavioral analytics into their platforms. It is not a matter of technology availability rather than dedication toward the 18-month implementation period for setting a baseline, tuning and optimization.
Companies that implement behavioral analytics today are five times quicker in going through threats and average cost reduction per year of 12,600,000 dollars. The ROI is not theory, it is quantified by the decrease in the frequency of incidents, accelerated containment and increase productivity of the analysts.
The autonomous AI agents that will be faced with the shared responsibility of the threat hunting and machine speed response are already in play. To counter attacks by AI, artificial intelligence needs artificial intelligence. The implementation time window is shrinking as the sophistication of attacks is increasing fast.
Begin with a single use case that is important. Implement insider threat or credentials abuse verification. Take the background/Initial false positive rates and take the new tuning methodically over a couple of months. It is these organisations that take the path now that will be around when the next wave of automated AI-driven attacks strike.
Gone are the days of human speed security and reactive security. The new survival level is behavioral analysis that is fueled by AI.
I’m a technology writer with a passion for AI and digital marketing. I create engaging and useful content that bridges the gap between complex technology concepts and digital technologies. My writing makes the process easy and curious. and encourage participation I continue to research innovation and technology. Let’s connect and talk technology!



